Deep Decarbonization Pathways Approach
In-country experts of the Deep Decarbonization Pathways (DDP) network build and bring to the public debate country-driven pathways, ie. analyses of national transformations consistent with deeply reducing GHG emissions as required by global carbon neutrality and satisfying development priorities as defined in each country context.
The pathways are developed following the principles of the DDP approach, operationalized in a common pathway design framework used to design and compare pathways across geographies and sectors.
The DDP pathway design framework allows:
- building qualitative narratives around the comprehensive consideration of decarbonization drivers and feasibility conditions
- translating the narrative into quantified pathways through a combination of analytical methods and expert assessments
- enabling the transparent communication of underlying drivers and assumptions and their comparison across countries thanks to standardized quantitative outputs.
The comparability is important because it allows a constructive debate among stakeholders with different interests within a country, as well as on an international level. Knowing and understanding the strategies of other countries allows to learn from each other and to identify useful cooperation areas.
The DDP methodology comprises five steps:
- Storyline – Developing a consistent narrative of the transition that describes the evolution of decarbonization drivers covering the economic, demographic, technical, organizational, and behavioral dimensions.
- Computation – Compiling these assumptions, ensuring consistency, and calculating their effects through detailed indicators. These calculations can be done through different modelling tools, expert-based assessments and other quantitative assessment methods. Some sectoral DDP tools propose a user-friendly approach to this step.
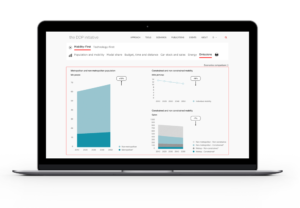
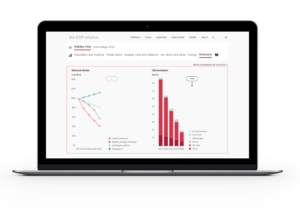
- Dashboard – Providing a quantitative representation of the pathway, showing its components and effects, through selected indicators.
- Check – Verifying the consistency of the pathway based on the indicators across its interrelated assumptions. In case of inconsistencies, the design should return to step 1.
- Communication – Communication – Visualizing the pathway and its key elements with graphs.
Key publications about the DDP approach and methodology:
- The need for national deep decarbonization pathways for effective climate policy (link)
- A pathway design framework for national low greenhouse gas emission development strategies (link)
- A pathway design framework for sectoral deep decarbonization: the case of passenger transportation (link)
- A low GHG development pathway design framework for agriculture, forestry and land use (link)
- A pathway design framework for sectoral deep decarbonization: the case of freight transportation, submitted and under review
Explore Current Policy and Deep Decarbonization scenarios
The DDP has developed its own pathway visualization tool, during its first project ahead of COP21. For 16 of the largest emitting countries, it displayed several deep decarbonization pathways proposed by DDP in-country research teams.
Today, this website hosts a third-generation pathway visualization tool that integrates new knowledge and enables to cover different sectors. Please click below to visualize the scenarios developed through DDP projects, namely DDP LAC, DDP ACT, DDP Transport, DDP BIICS and IMAGINE (currently in development).